What is narrative?
In media terms, narrative is the
organisation given to a series of facts. Everything in media has a narrative.
Our mind requires narrative in order to make sense of things. We
connect events and make an understanding based on the links. In everything we
seek a beginning, middle and end. We understand and create meaning using your
texts. Each text becomes part of the previous.
Many people get confused between the story and the narrative. The story
is a sequence of events known as the plot, while the narrative is the way those
events are put together, to be presented to us, the audience.
When looking into narrative you also need to think about what the
story is about in its most basic terms, the theme, for example Love or war etc.
Narratives can be re used and have been re used a lot especially
in super hero movies and in romantic movies as well
There are 4 different theorists, who have been very influential
in the world of media.
Todorov
Todorov
was a Bulgarian philosopher who proposed that all narratives falls into
standard 3 part structure:
- They
begin with equilibrium, where everything is balanced
- Then
disequilibrium, this is when something comes along to disrupt that equilibrium
- Finally,
is the resolution, which is a new equilibrium
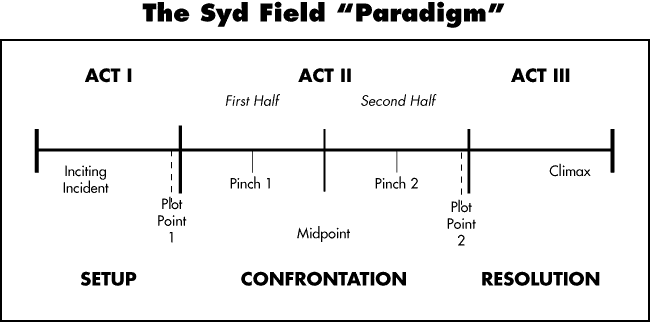
Syd Field
Syd
Field is regarded by many Hollywood professionals to be the leading authority I
the art. He believes a narrative is split onto 3 acts. This is based on Todorovs
theory but Filed has had his own take to it. Below is an example of Syd Field's narrative structure:
Vladmir
Propp was a Russian formalist who analyzed the basic plot components of Russian
folk tales to identify their simplest irreducible narrative elements.
Propp
constructed a list of 31 functions and character types:
The Hero: leads the
narrative, is usually looking for something like a quest or trying to solve something
like a mystery. Examples of heroes are: Superman and Batman, who are well
known. Even though a hero has been thought to be only male, there are females
who also play a part in being a hero such as Wonder Woman and Catwoman.
 |
| The Joker in 'Batman' |
The Villain: has
a conflict with the hero and tries to stop them complete their mission and succeeding.
For example, the Joker in Batman, and
the Green Goblin in Spiderman.
The Doner:
gives the hero something, like a special power, ability, which aids them
complete their quest. For example, like in Star
Wars, Obi-wan Kenobi mentored and
taught Luke Skywalker everything, so
that he could become a jedi. Another example, in Iron, the doctor who built a device which kept Tony Stark (Ironman) alive; it acted as a heart. Then he went on to
become Ironman form then.
The Princess:
is usually a pride or reward for the hero. However, if the hero is female,
there can ebbs a price but this is unusual. An example is, is Princess Fiona in Shrek, when Shrek had to rescue her.
 |
| Princess Fiona in 'Skrek' |
 |
| Donkey in 'Skrek' |
The Helper:
helps the hero, especially at times at need, acts as a sidekick. For example, Robin was Batman’s sidekick in a few of the Batman films. Another example is Donkey in Shrek, as Donkey was always there for Shrek.
The Princes’ Fathers:
a figure who lays down authority and who offers a reward to the hero for completing
their quest. That reward might be the prince or the princess or in some cases
money, because the princess’ father can be seen as a false hero.
The False Hero:
the false hero takes credit for the hero has done, taking credit for his actions,
if though he didn’t do anything. Furthermore or he tries to marry the princess
to someone she may not like or favour. For example, when Princess Fiona was forced to marry Prince Charming, and in the film he was trying to make out he was
the hero.
 |
| Prince Charming in 'Skrek' |
The Dispatcher:
the character who sets the hero off.
Another narrative theory is Roland Barthes'.
Roland Barthes
Roland Barthes was a french semiologist. he suggested that narrative works with five different codes which motivates the reader to make sense of it.
Barthes Codes:
Action - a narrative device which a resolution by produced through action. for example a shoot out
Enigma - a narrative device that teases the audience by presenting a puzzle or riddle to be solved. This works very well as it makes the ending of the story very pleasurable.
Symbolic - (connotation)
Semic - (denotation)
Cultural - a narrative device which the audience can recognize as being part of a culture. For example, the culture 'made man' in a gangster film.
When a narrative is constructed in the order of events it is called Linear. However, when a narrative is constructed out of order, meaning it may go back and forward in time or have flashbacks, this is called Non-Linear.
Another narrative theory I learnt about was Claude Levi-Strauss' theory called the 'Binary Opposition'
Levi-Strauss was a social anthropologist. He studied myths of tribal culture. He examined how stories unconsciously reflect the values, beliefs and myths of a culture. These are usually expressed by the form of binary opposition. His research has adopted media theorists to reveal underlying themes and symbolic oppositions media texts.
These are xamples of Levi-Strauss; theory:
Homesteads Vs Native America
Christians Vs Pagans
Domestic Vs Savage
Weak vs Strong
Garden Vs Wilderness
Inside Society Vs Outside Society